import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# Retina mode
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
%matplotlib inlineBasis Expansion in Linear Regression
ML
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100)from sklearn.kernel_approximation import RBFSamplerRBFSampler?Init signature: RBFSampler(*, gamma=1.0, n_components=100, random_state=None) Docstring: Approximate a RBF kernel feature map using random Fourier features. It implements a variant of Random Kitchen Sinks.[1] Read more in the :ref:`User Guide <rbf_kernel_approx>`. Parameters ---------- gamma : 'scale' or float, default=1.0 Parameter of RBF kernel: exp(-gamma * x^2). If ``gamma='scale'`` is passed then it uses 1 / (n_features * X.var()) as value of gamma. .. versionadded:: 1.2 The option `"scale"` was added in 1.2. n_components : int, default=100 Number of Monte Carlo samples per original feature. Equals the dimensionality of the computed feature space. random_state : int, RandomState instance or None, default=None Pseudo-random number generator to control the generation of the random weights and random offset when fitting the training data. Pass an int for reproducible output across multiple function calls. See :term:`Glossary <random_state>`. Attributes ---------- random_offset_ : ndarray of shape (n_components,), dtype={np.float64, np.float32} Random offset used to compute the projection in the `n_components` dimensions of the feature space. random_weights_ : ndarray of shape (n_features, n_components), dtype={np.float64, np.float32} Random projection directions drawn from the Fourier transform of the RBF kernel. n_features_in_ : int Number of features seen during :term:`fit`. .. versionadded:: 0.24 feature_names_in_ : ndarray of shape (`n_features_in_`,) Names of features seen during :term:`fit`. Defined only when `X` has feature names that are all strings. .. versionadded:: 1.0 See Also -------- AdditiveChi2Sampler : Approximate feature map for additive chi2 kernel. Nystroem : Approximate a kernel map using a subset of the training data. PolynomialCountSketch : Polynomial kernel approximation via Tensor Sketch. SkewedChi2Sampler : Approximate feature map for "skewed chi-squared" kernel. sklearn.metrics.pairwise.kernel_metrics : List of built-in kernels. Notes ----- See "Random Features for Large-Scale Kernel Machines" by A. Rahimi and Benjamin Recht. [1] "Weighted Sums of Random Kitchen Sinks: Replacing minimization with randomization in learning" by A. Rahimi and Benjamin Recht. (https://people.eecs.berkeley.edu/~brecht/papers/08.rah.rec.nips.pdf) Examples -------- >>> from sklearn.kernel_approximation import RBFSampler >>> from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier >>> X = [[0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 0], [0, 1]] >>> y = [0, 0, 1, 1] >>> rbf_feature = RBFSampler(gamma=1, random_state=1) >>> X_features = rbf_feature.fit_transform(X) >>> clf = SGDClassifier(max_iter=5, tol=1e-3) >>> clf.fit(X_features, y) SGDClassifier(max_iter=5) >>> clf.score(X_features, y) 1.0 File: ~/miniforge3/lib/python3.9/site-packages/sklearn/kernel_approximation.py Type: type Subclasses:
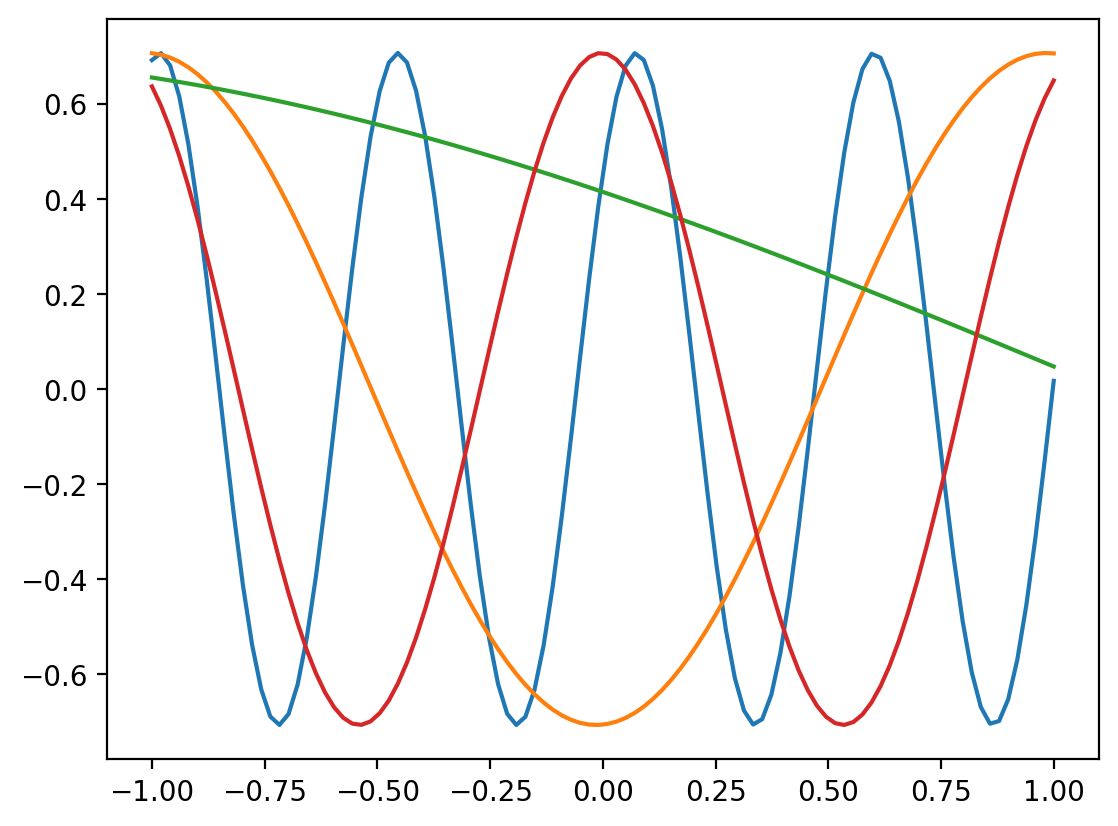
r= RBFSampler(n_components=5)plt.plot(x, r.fit_transform(x.reshape(-1,1)))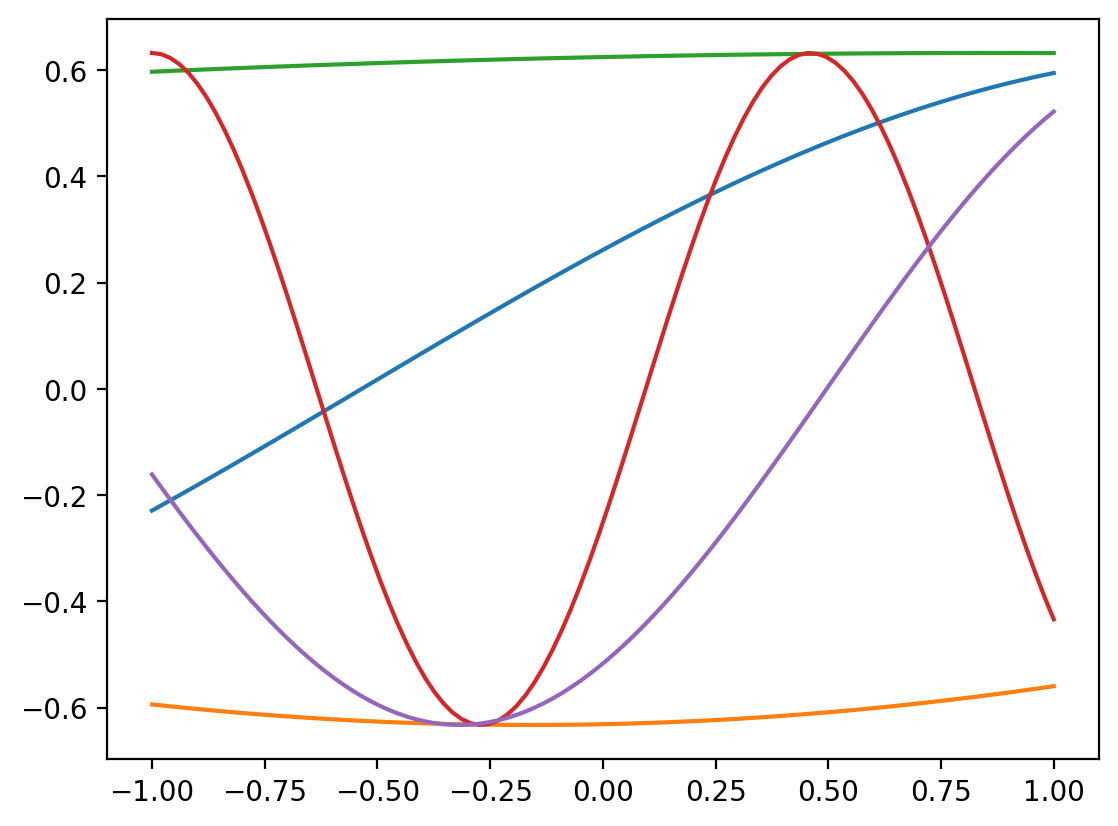
r = RBFSampler(n_components=4, gamma=0.1)
plt.plot(x, r.fit_transform(x.reshape(-1,1)))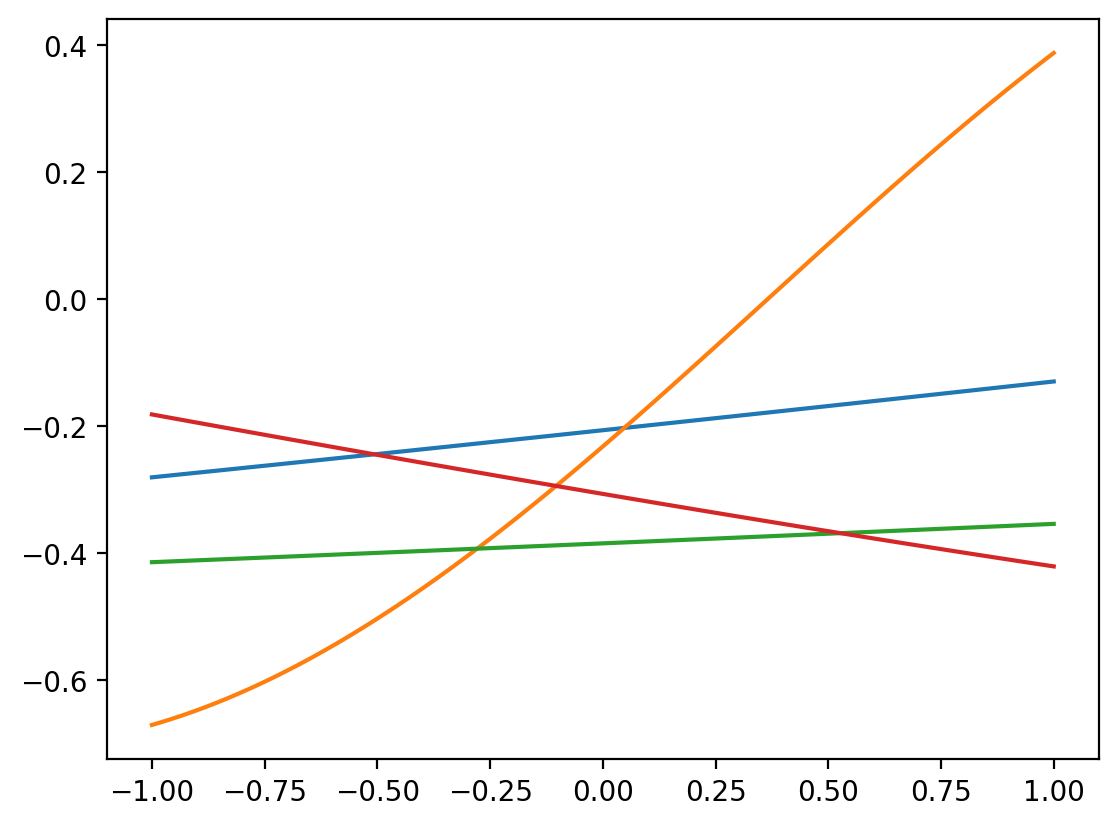
r = RBFSampler(n_components=4, gamma=20)
plt.plot(x, r.fit_transform(x.reshape(-1,1)))