import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'SVM Kernel
SVM Kernel
X = np.array([-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]).reshape(-1, 1)
y = np.array([-1, -1, 1, 1, 1, -1, -1])plt.scatter(X.flatten(), np.zeros_like(X), c=y, cmap=cm.Paired)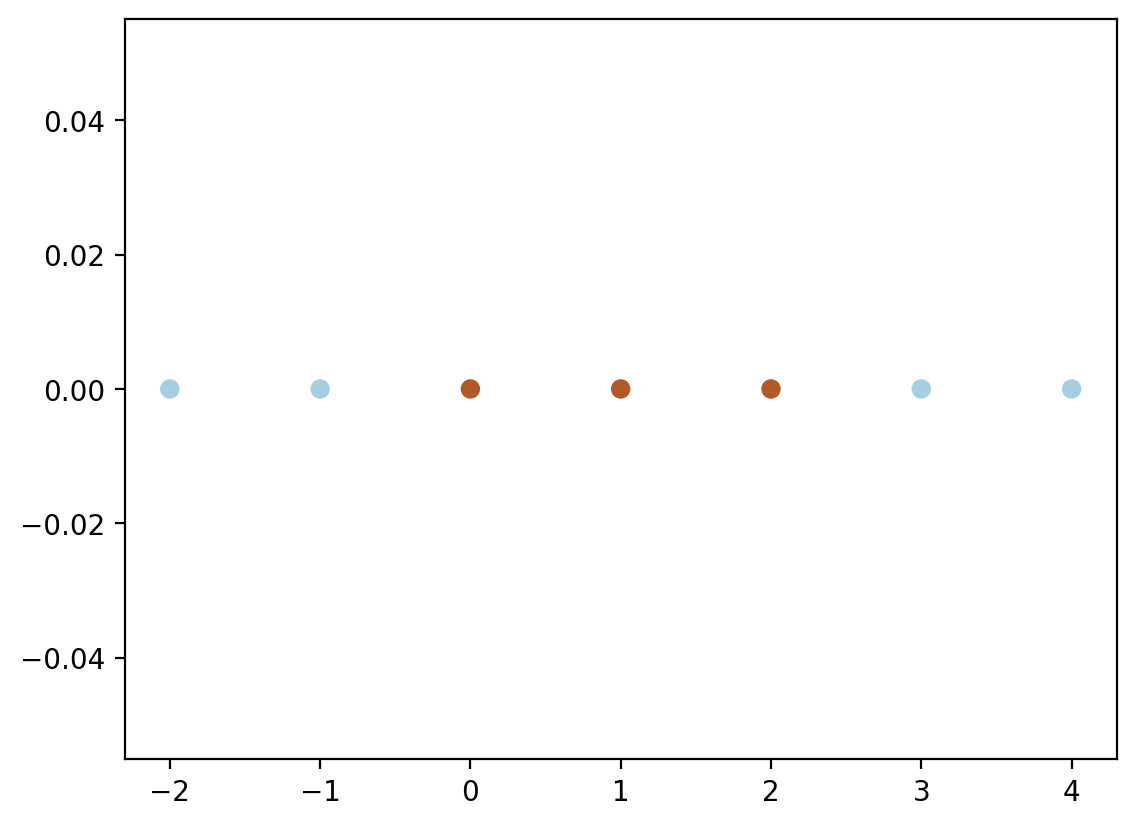
def phi(x):
return np.hstack([x, x**2])phi(X)array([[-2, 4],
[-1, 1],
[ 0, 0],
[ 1, 1],
[ 2, 4],
[ 3, 9],
[ 4, 16]])plt.scatter(phi(X)[:, 0], phi(X)[:, 1], c = y,cmap = cm.Paired)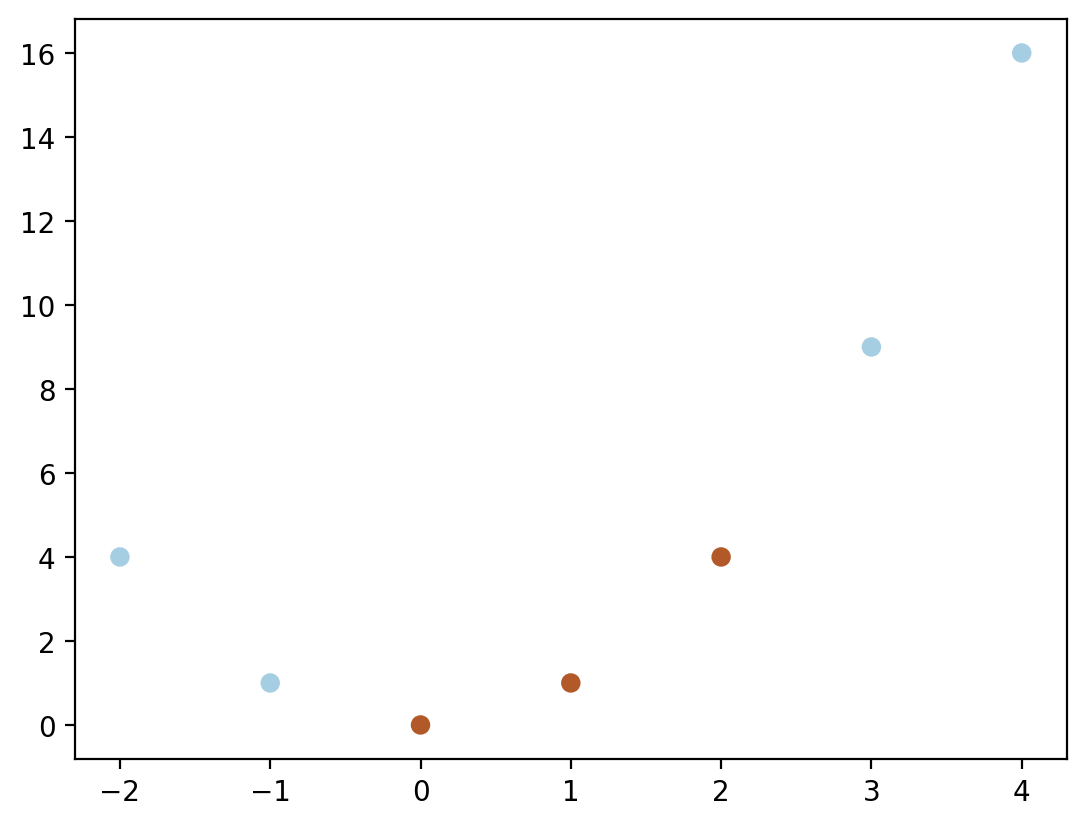
from sklearn.svm import SVCc = SVC(kernel='linear', C = 1e6)c.fit(phi(X), y)SVC(C=1000000.0, kernel='linear')In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
SVC(C=1000000.0, kernel='linear')
plt.scatter(phi(X)[:, 0], phi(X)[:, 1], c = y, zorder=10, cmap =cm.Paired, edgecolors='k', alpha=1, s=200)
x_min = phi(X)[:, 0].min()-1
x_max = phi(X)[:, 0].max()+1
y_min = phi(X)[:, 1].min()-1
y_max = phi(X)[:, 1].max()+1
XX, YY = np.mgrid[x_min:x_max:200j, y_min:y_max:200j]
Z = c.decision_function(np.c_[XX.ravel(), YY.ravel()])
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(XX.shape)
plt.pcolormesh(XX, YY, Z > 0, cmap=plt.cm.Paired, alpha=0.6)
plt.contour(XX, YY, Z, colors=['k', 'k', 'k'],
linestyles=['--', '-', '--'], levels=[-1, 0, 1])
plt.xlabel(r"$x_1 = X$")
plt.ylabel(r"$x_2 = X^2$")
plt.title(r"Decision surface: {:0.1f}*x_1 + {:0.1f}*x_2 + {:0.1f} = 0".format(c.coef_[0, 0], c.coef_[0, 1], c.intercept_[0]))Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Decision surface: 1.3*x_1 + -0.7*x_2 + 1.0 = 0')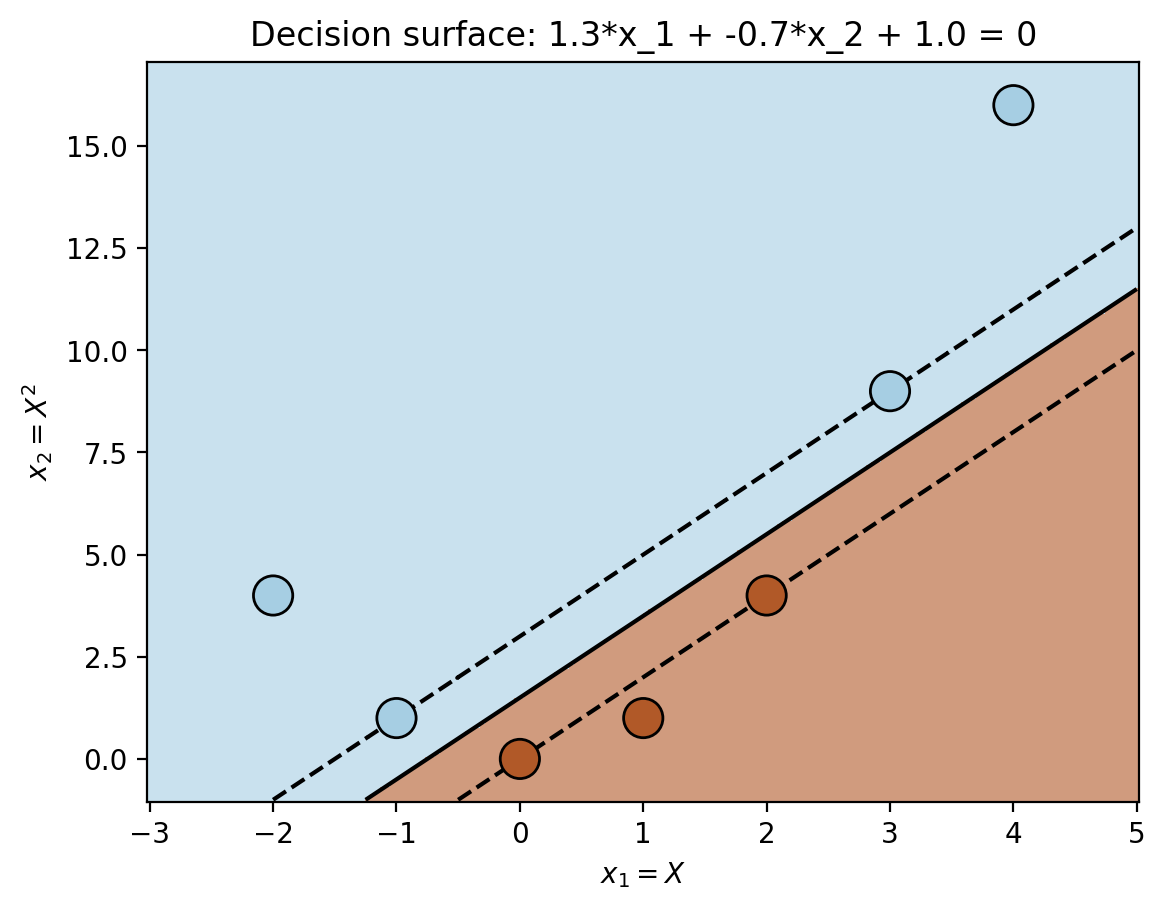
# Now using non-linearly separable data in 2D
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs, make_circles
X, y = make_circles(n_samples=100, factor=0.5, noise=0.4)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=cm.Paired)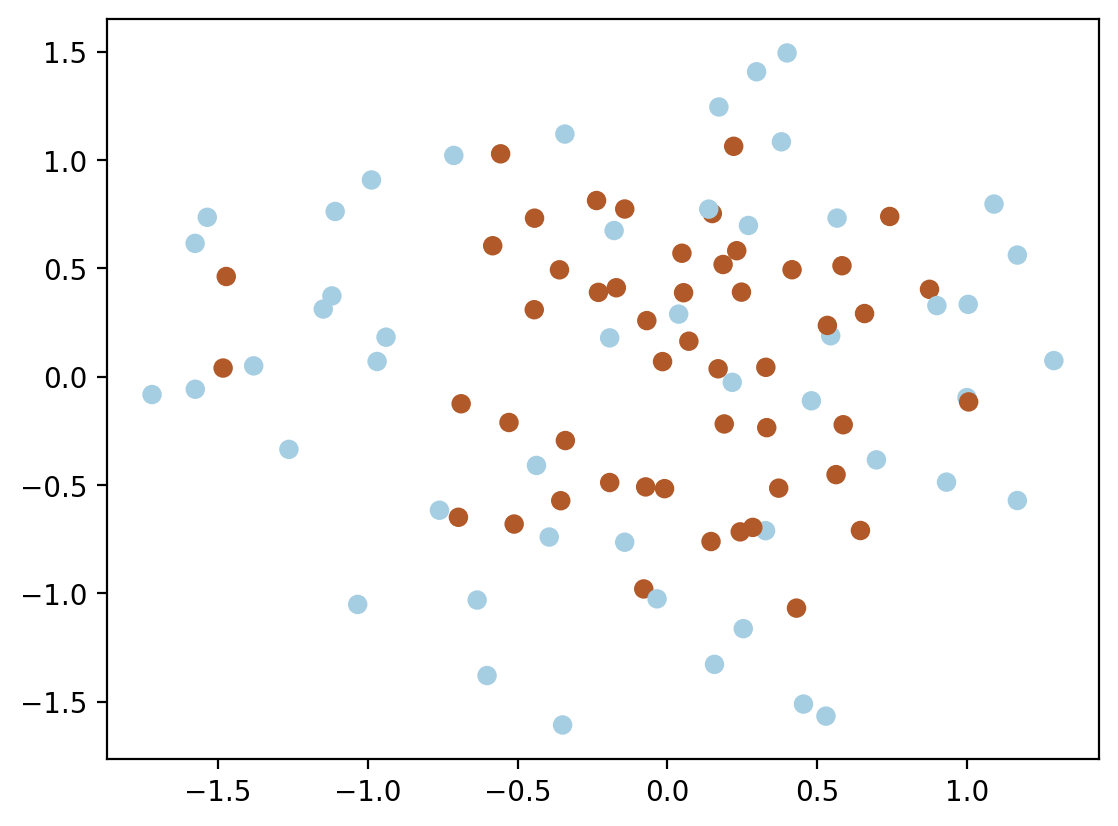
def plot_contour(X, y, clf):
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(X[:, 0].min(), X[:, 0].max(), 40), np.linspace(X[:, 1].min(), X[:, 1].max(), 40))
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, colors='k', levels=[-1, 0, 1], alpha=0.9,
linestyles=['--', '-', '--'])
plt.scatter(c.support_vectors_[:, 0], c.support_vectors_[:, 1], s=100,
linewidth=1, facecolors='none', edgecolors='k')
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, cmap=cm.Paired)
plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z > 0, cmap=plt.cm.Paired, alpha=0.2)
# Train accuracy
y_pred = clf.predict(X)
plt.title("Train accuracy: {:0.2f}\n Number of support vectors: {}".format((y_pred == y).mean(), len(clf.support_vectors_)))
# First linear SVM
c = SVC(kernel='linear', C=10)
c.fit(X, y)
plot_contour(X, y, c)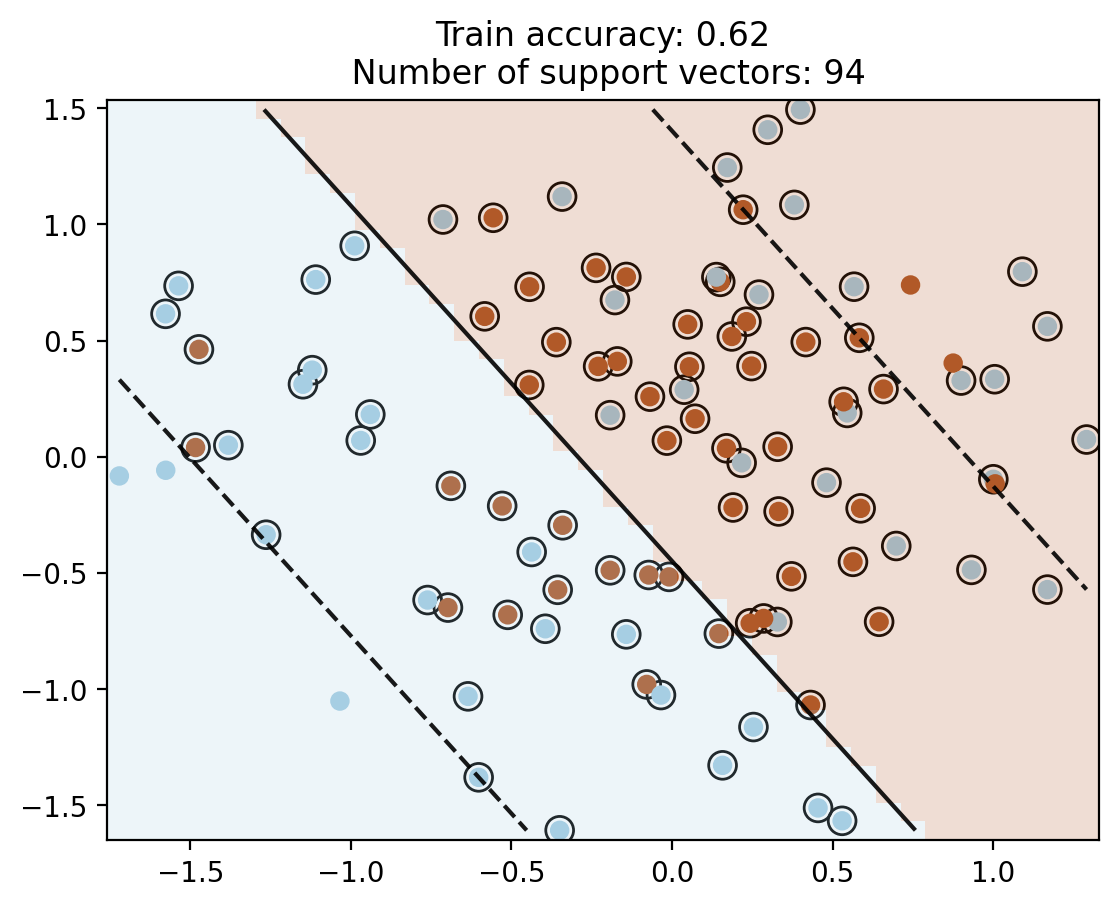
c_poly2 = SVC(kernel='poly', degree=2, C=10)
c_poly2.fit(X, y)
plot_contour(X, y, c_poly2)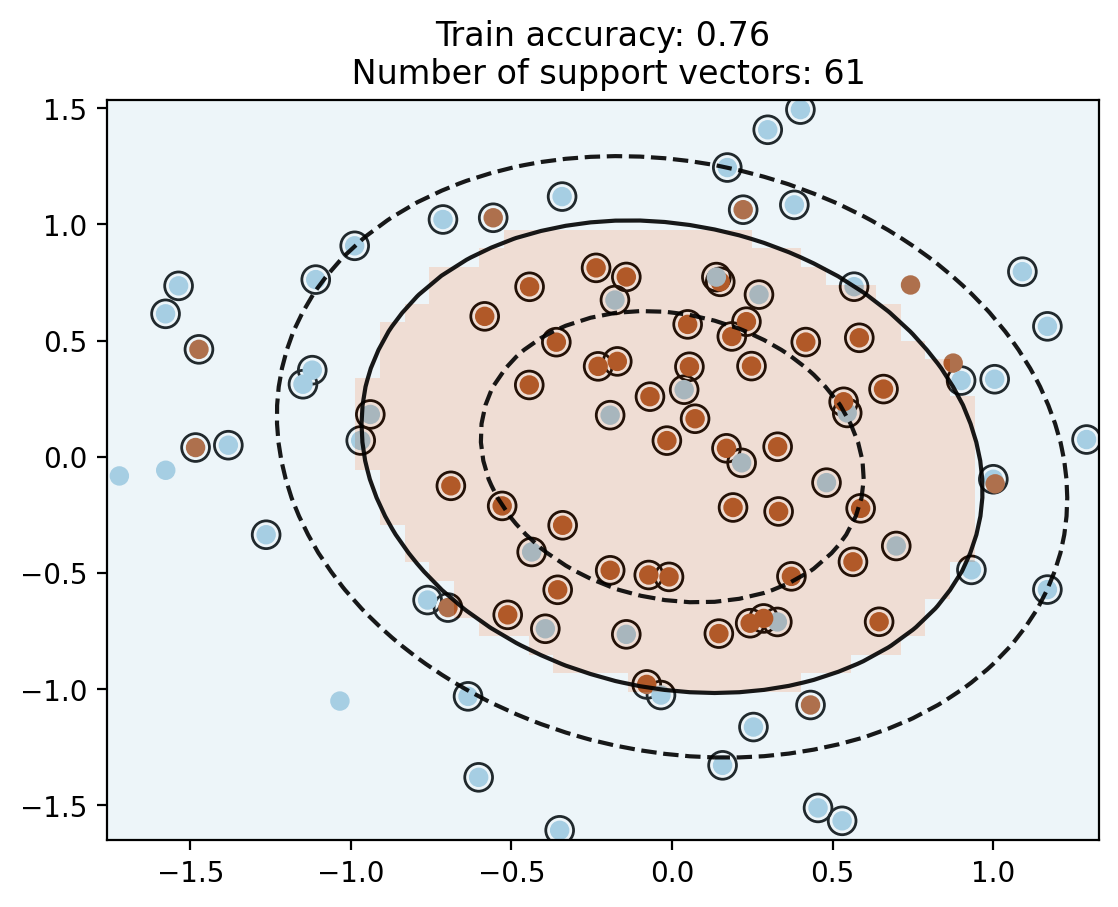
# RBF kernel
c_rbf = SVC(kernel='rbf', C=10, gamma=1e-1)
c_rbf.fit(X, y)
plot_contour(X, y, c_rbf)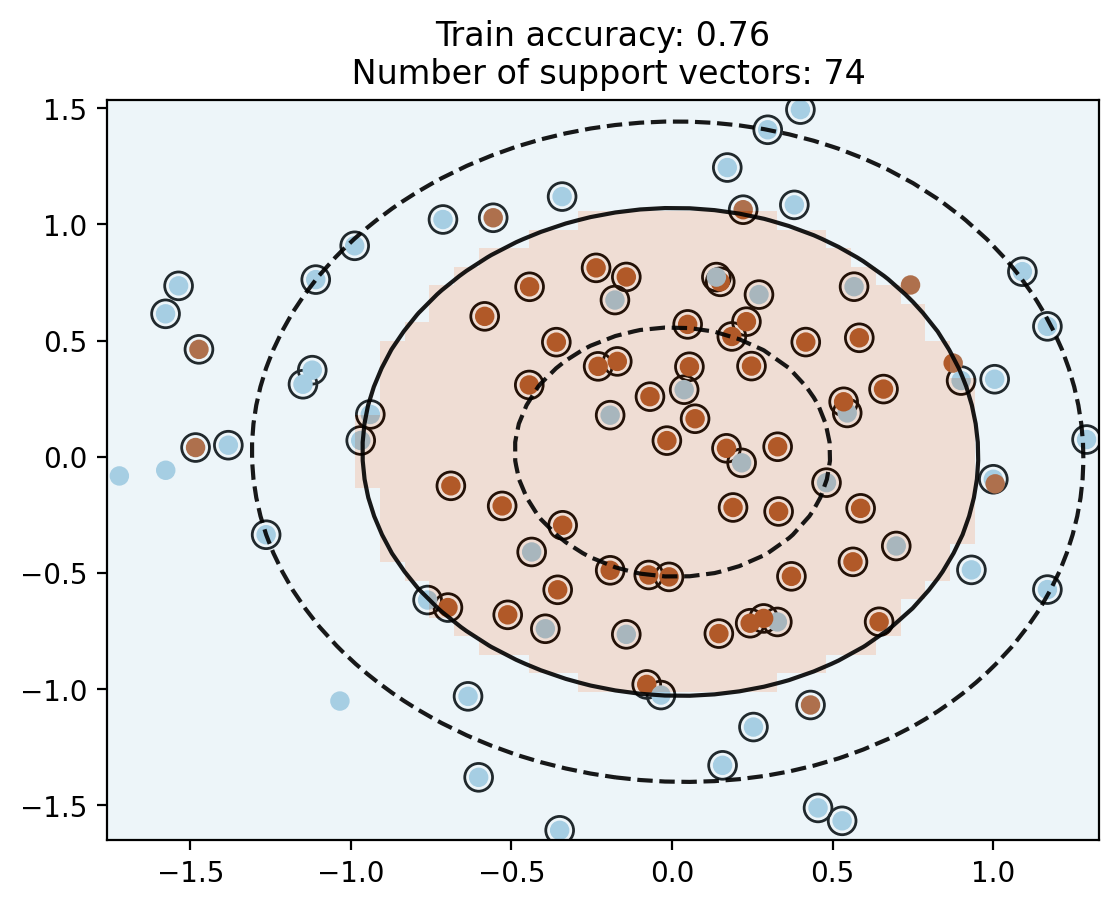
# interactive widget to show the effect of gamma
from ipywidgets import interact
def plot_svm(gamma=0.05):
c = SVC(kernel='rbf', C=10, gamma=gamma)
c.fit(X, y)
plot_contour(X, y, c)
interact(plot_svm, gamma=(0.01, 60, 0.05))<function __main__.plot_svm(gamma=0.05)>