import numpy as np
import sklearn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
%matplotlib inlinehttps://towardsdatascience.com/introduction-to-reliability-diagrams-for-probability-calibration-ed785b3f5d44
p = np.array([0.9, 0.2, 0.7, 0.4, 0.8, 0.1, 0.2, 0.8, 0.5, 0.9])true_labels = np.ones_like(p)
true_labels[[1, 6, 7, 8]] = 0
true_labelsarray([1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 1.])num_splits = 3splits_arr = np.linspace(0, 1, num_splits + 1)
splits = [(x, y) for (x, y) in zip(splits_arr[:-1], splits_arr[1:])]
splits[(0.0, 0.3333333333333333),
(0.3333333333333333, 0.6666666666666666),
(0.6666666666666666, 1.0)]pd.cut(pd.Series(p), bins=splits_arr)0 (0.667, 1.0]
1 (0.0, 0.333]
2 (0.667, 1.0]
3 (0.333, 0.667]
4 (0.667, 1.0]
5 (0.0, 0.333]
6 (0.0, 0.333]
7 (0.667, 1.0]
8 (0.333, 0.667]
9 (0.667, 1.0]
dtype: category
Categories (3, interval[float64, right]): [(0.0, 0.333] < (0.333, 0.667] < (0.667, 1.0]]splits = np.digitize(p, splits_arr)
splitsarray([3, 1, 3, 2, 3, 1, 1, 3, 2, 3])p_group = {}
labels_pos = {}
for group in np.unique(splits):
p_group[group] = p[splits==group]
#frac_pos[group] = true_labels[splits==group].sum()*1.0/len(p_group[group])
labels_pos[group] = true_labels[splits==group]
#print(np.arange(10)[splits==group])p_group{1: array([0.2, 0.1, 0.2]),
2: array([0.4, 0.5]),
3: array([0.9, 0.7, 0.8, 0.8, 0.9])}labels_pos{1: array([0., 1., 0.]), 2: array([1., 0.]), 3: array([1., 1., 1., 0., 1.])}p_group_mean = {k:np.mean(v) for k, v in p_group.items()}
p_group_mean{1: 0.16666666666666666, 2: 0.45, 3: 0.8200000000000001}fracs = {k:np.sum(v)*1.0/len(v) for k, v in labels_pos.items()}
fracs{1: 0.3333333333333333, 2: 0.5, 3: 0.8}plt.plot(p_group_mean.values(), fracs.values(), marker='*')
plt.xlim((-0.05, 1.05))
plt.ylim((-0.05, 1.05))
plt.gca().set_aspect("equal")
plt.xlabel("p")
plt.ylabel("Relative frequency")
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='k', ls='--', label='Ideal')
plt.legend()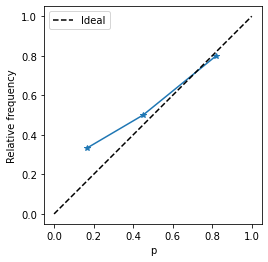
Let us wrap into a function
def calib_curve(true, pred, n_bins = 10):
splits_arr = np.linspace(0, 1, n_bins + 1)
splits = np.digitize(pred, splits_arr)
p_group = {}
labels_pos = {}
for group in np.unique(splits):
p_group[group] = pred[splits==group]
labels_pos[group] = true[splits==group]
p_group_mean = {k:np.mean(v) for k, v in p_group.items()}
fracs = {k:np.sum(v)*1.0/len(v) for k, v in labels_pos.items()}
counts = np.array([len(v) for v in labels_pos.values()])
return np.array(list(p_group_mean.values())), np.array(list(fracs.values())), countsfrom sklearn.calibration import calibration_curve, CalibrationDisplay
prob_true, prob_pred = calibration_curve(true_labels, p, n_bins=3)prob_truearray([0.33333333, 0.5 , 0.8 ])prob_predarray([0.16666667, 0.45 , 0.82 ])p_ours, p_hat_ours, count = calib_curve(true_labels, p, 3)
p_oursarray([0.16666667, 0.45 , 0.82 ])Expected Calibration Error
(np.abs(p_ours-p_hat_ours)*count).mean()0.23333333333333336from sklearn.datasets import make_classificationX, y = make_classification(n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, random_state=0)plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c = y)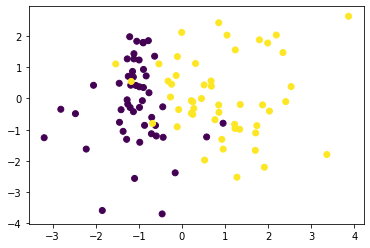
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionlr = LogisticRegression()lr.fit(X, y)LogisticRegression()In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LogisticRegression()
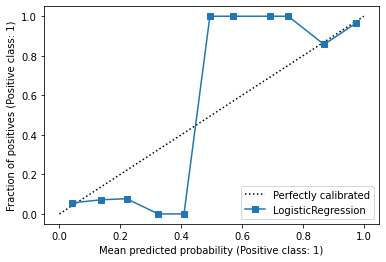
display = CalibrationDisplay.from_estimator(
lr,
X,
y,
n_bins=11,
)
pred_p = lr.predict_proba(X)[:, 1]probs, fractions, counts = calib_curve(y, pred_p, 11)plt.plot(probs, fractions, marker='^')
plt.xlabel("p")
plt.ylabel("Relative frequency")
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='k', ls='--', label='Ideal')
plt.legend()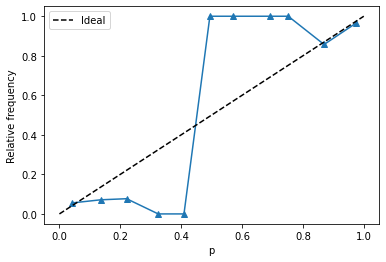
plt.hist(pred_p);
(np.abs(probs-fractions)*counts).mean()0.9530316314463302countsarray([18, 14, 13, 4, 2, 4, 2, 2, 6, 7, 28])